Project 1.5.2: Red Blink¶
| Description | This project is one that makes emphasis on how to create a simple circuit and to control the red light on the RGB to blink beautifully. |
|---|---|
| Use case | Wanting to create an interactive lighting system for your school using as a security and safety alert light, you can program the Red LED in the RGB alone to blink indicating danger whenever there’s an intruder. |
Components (Things You will need)¶
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
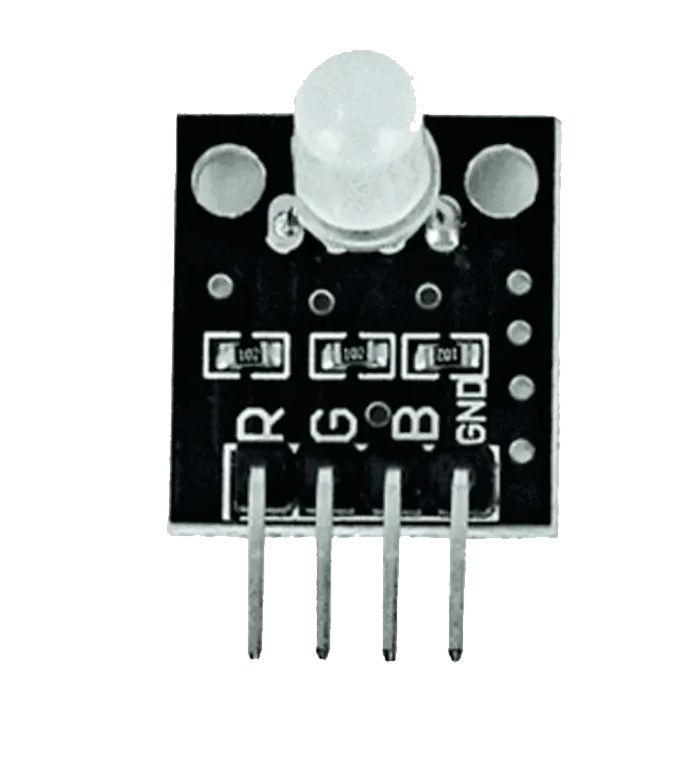 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Building the circuit¶
Things Needed:
- Arduino Uno Board = 1
- Arduino USB cable = 1
- RGB= 1
- Red jumper wires = 1
- White jumper wires = 1
Mounting the component on the breadboard¶
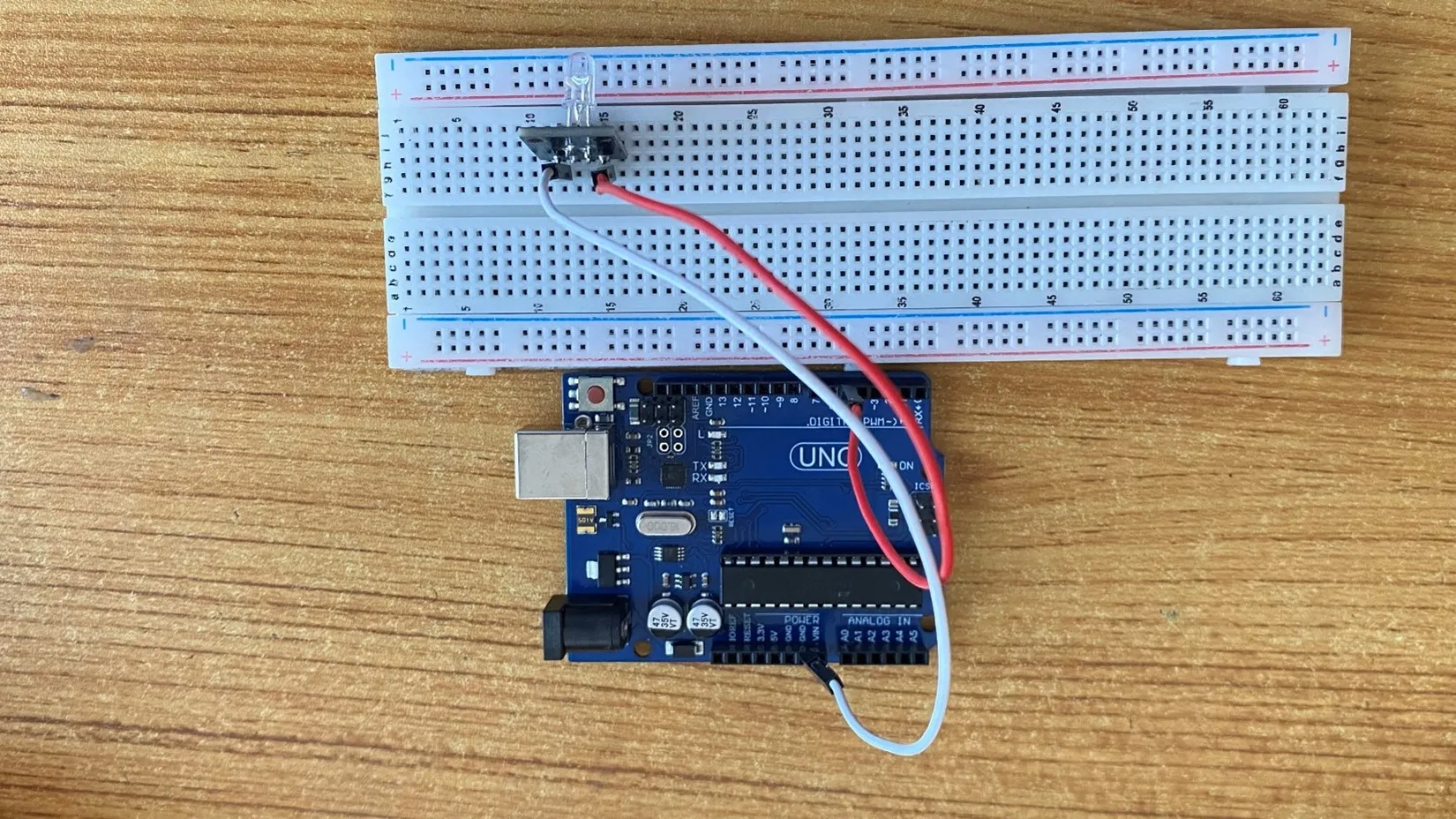
Step 1: The RGB module has four pins, R pin(red), G pin(green), B pin(blue) and – pin (GND). On the middle section of the breadboard, locate each horizontal section lettered A to J. Take the RGB module and insert it into any of the lettered section (Say A) horizontally.
NB: Take note of where each of the pins of the RGB are placed on the bread board.
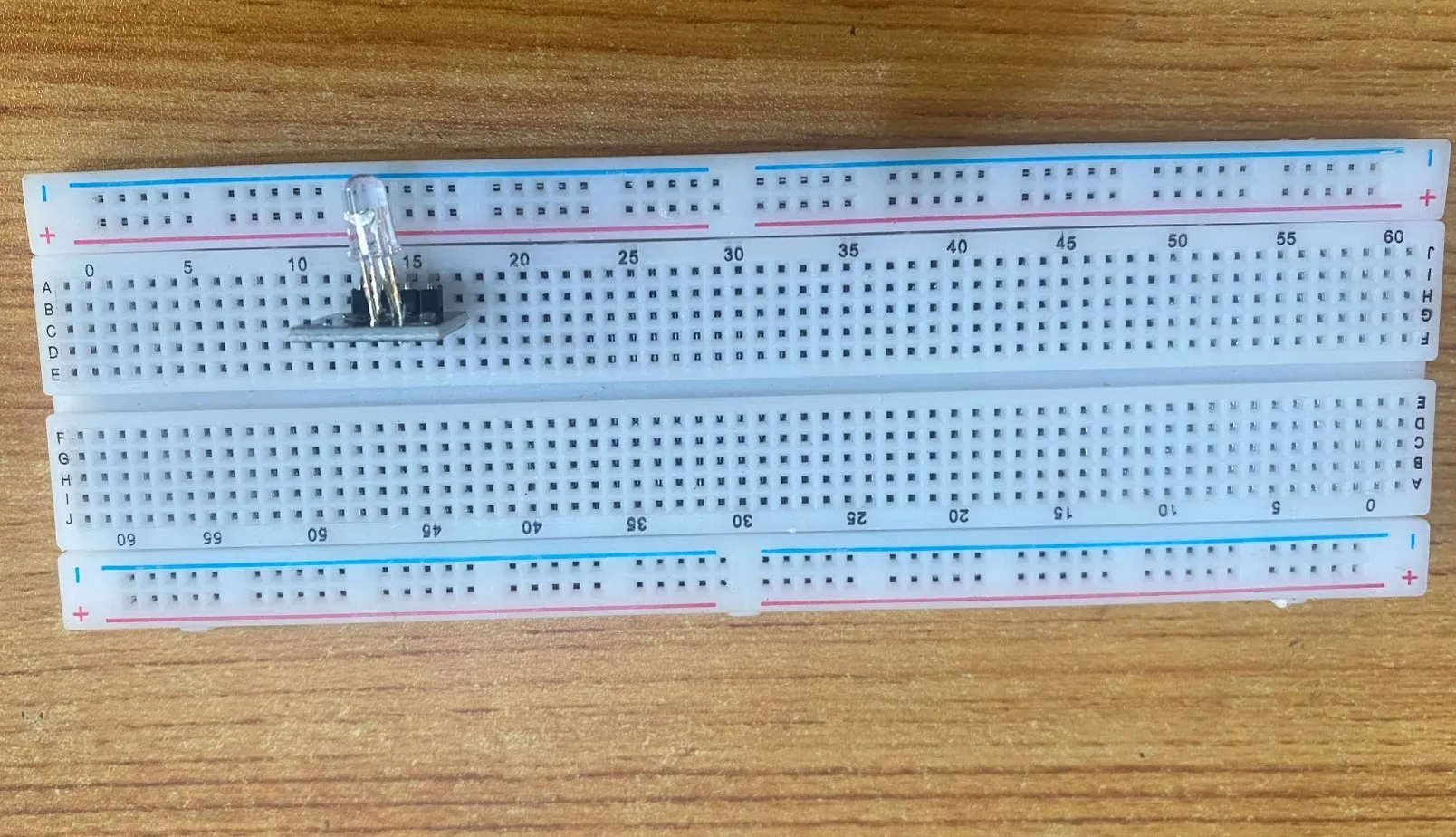 .
.
WIRING THE CIRCUIT¶
Things Needed:
- Red jumper wire = 1
- white jumper wire = 1
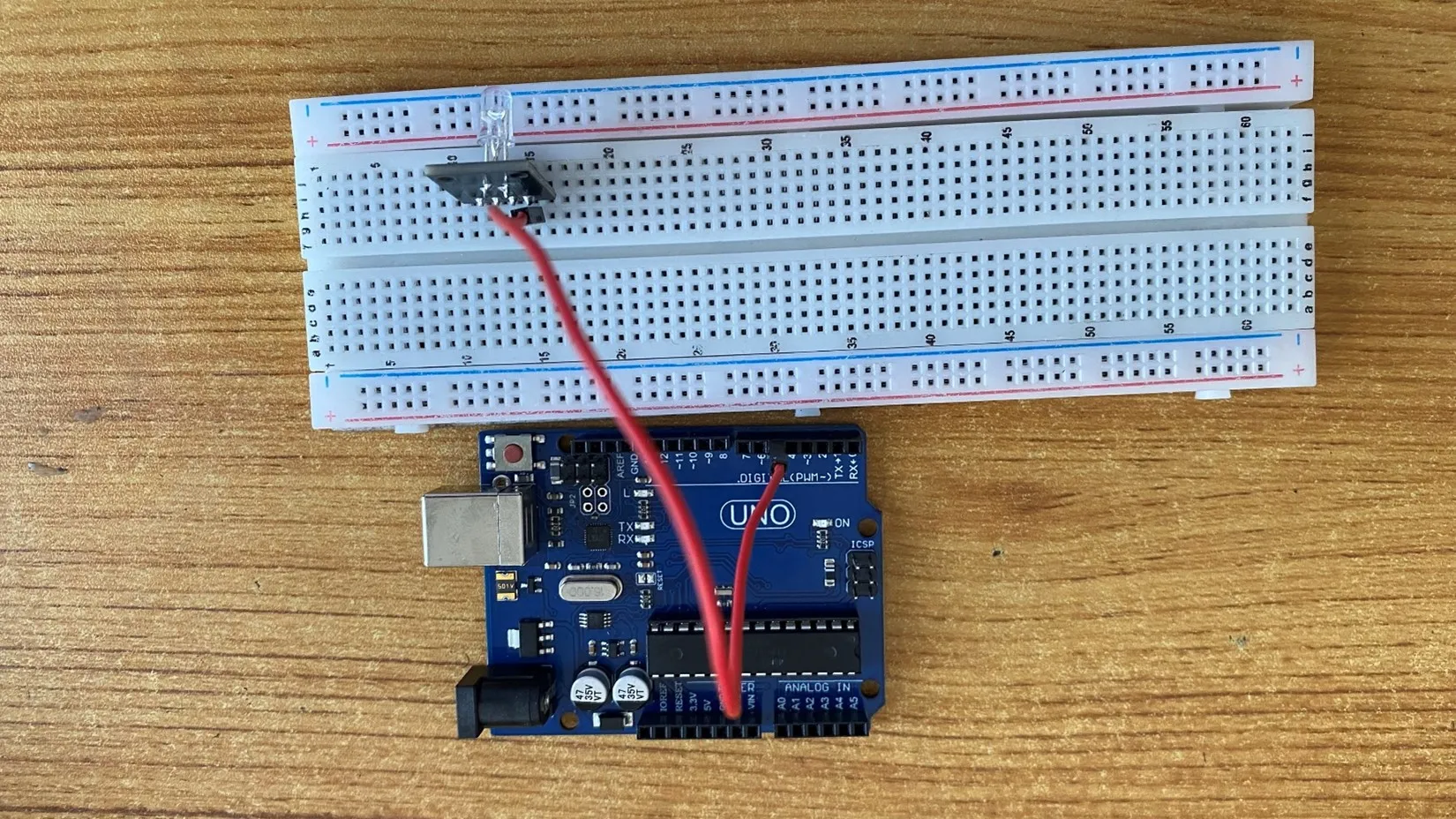
Step 2: Take the red jumper wire. This wire will connect the Arduino UNO and the R pin of the RGB module.
-
Connect one end of the red jumper wire to R pin of RGB module on the breadboard. Ensure you put the pin in the right hole.
-
Connect the other end of the red jumper wire to pin number 5 on the Arduino UNO.
 .
.
Step 3: Take the white jumper wire and connect one end to the GND or the - pin of the RGB module.
- Connect the other end of the white jumper wire to GND on the Arduino UNO.
 .
.
PROGRAMMING¶
Step 1: Open your Arduino IDE. See how to set up here: Getting Started.
Step 2: Type const int red = 5; as shown below in the image.
NB: Make sure you avoid errors when typing. Do not omit any character or symbol especially the bracket { } and semicolons ; and put them as you see in the image. The code that comes after the two ash backslashes “//” are called comments. They are not part of the code that will be run, they only explain the lines of code. You can avoid typing them.
 .
.
Step 3: Type pinMode (red, OUTPUT); as shown below in the image.
 .
.
NB: The code below sets the pin names “red” as an output pin. An output pin helps send signals from the microcontroller to other components in the circuit. The pinMode () function, helps determine and control the behavior of a specific pin on the board
Step 4: Type digitalWrite (red, HIGH); as shown below in the image.
 .
.
The digitalWrite () function controls the state of the pin. The pin can either be HIGH or LOW. The HIGH state turns on the LED. As a result, the code below turns on the LED.
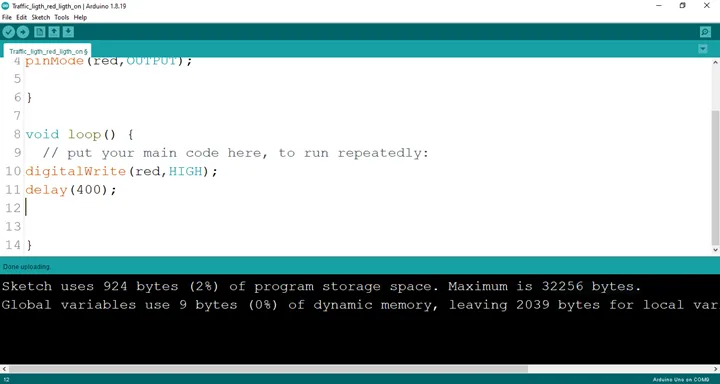
Step 5: Type delay (400); as shown below
 .
.
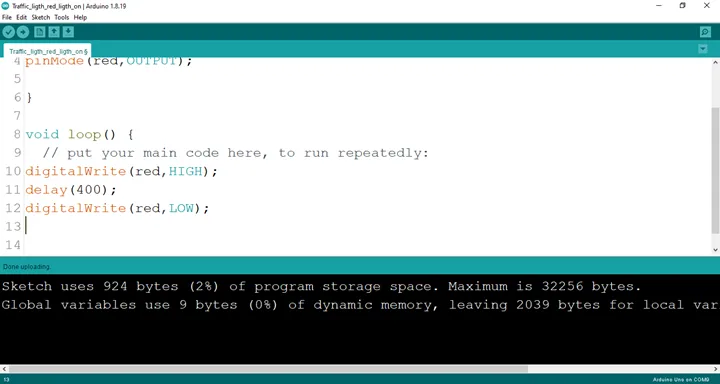
Step 6: Type digitalWrite (red, LOW); as seen below:
 .
.
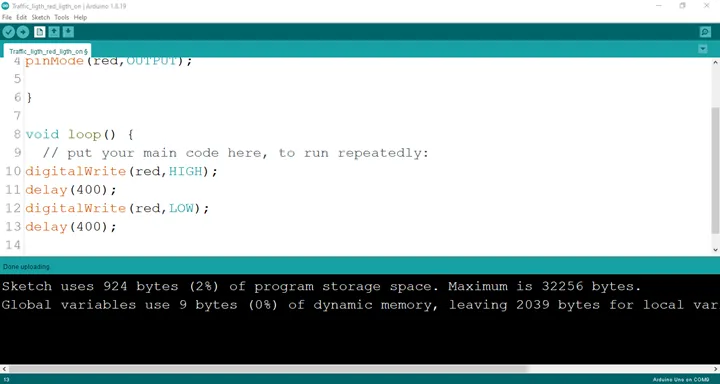
Step 7: Type delay (400); as shown below.
 .
.
Step 8: Save your code. See the Getting Started section
Step 9: Select the arduino board and port See the Getting Started section:Selecting Arduino Board Type and Uploading your code.
Step 10: Upload your code. See the Getting Started section:Selecting Arduino Board Type and Uploading your code
CONCLUSION¶
In summary, the project centered on creating a blinking red light within an RGB configuration provides an illuminating introduction to color manipulation and electronic control. By programming the red LED component to blink, participants acquire insights into timing control, code logic, and the dynamic visual effects of a single color. This endeavor serves as a pivotal step in exploring RGB color variation, showcasing the rhythmic potential of individual color components, and sparking interest in practical applications such as decorative lighting and visual aesthetics.